A Sub Title
About Title
- Important bullet points:
- Highlighted Fact #1
- Highlighted Fact #2
- Highlighted Fact #3
A Sub Title
A Second Section
Ut vel nisl ut risus feugiat faucibus. Sed ut est eget urna feugiat dictum. Aliquam urna eros, consequat in dictum venenatis, cursus eu orci. Suspendisse eget suscipit dui, et feugiat purus.
Ut neque lectus, porttitor vel leo a, hendrerit maximus felis. Ut consectetur nunc dui, vitae tincidunt leo volutpat ac. Nulla scelerisque scelerisque dapibus. Aliquam vel dapibus massa. Fusce auctor eros vel mi accumsan, vel egestas risus porttitor. Curabitur nec aliquam felis. Nunc ut blandit magna. Cras pharetra consectetur enim in ullamcorper. Ut posuere ultricies purus, sollicitudin bibendum turpis. Aliquam erat volutpat. Curabitur aliquam, neque eget dignissim porta, diam nunc tristique tortor, a condimentum lorem nisl vitae risus. Cras ipsum dui, sagittis ac ornare tristique, venenatis id dolor. Vestibulum eleifend interdum lacus in imperdiet. Class aptent taciti sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. Curabitur mollis facilisis lacus at vestibulum. Vestibulum sed facilisis urna.
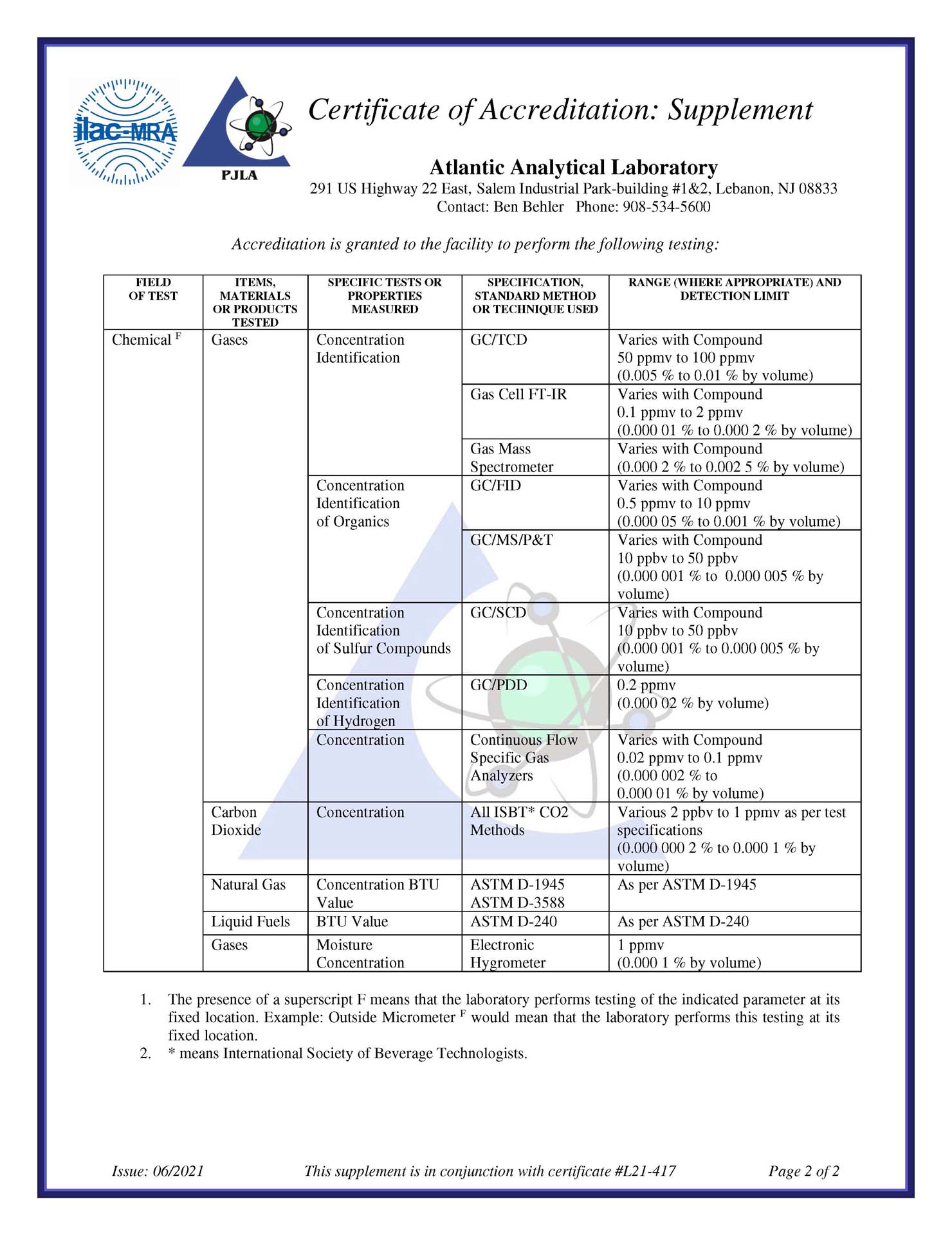
D.L.I., D.G.I., And H.S.I.
Sample Introduction Techniques
We have numerous GC’s with a wide array of sample introduction and detection techniques at our disposal. Many of them are dedicated systems while some can be configured to an individual need and validated to comply with cGMP.
Sample introduction techniques are Direct Liquid Injection (DLI), Direct Gas Injection (DGI), and Headspace Injection (HSI).
The heart of the GC is its column and chemistry, and we can handle both conventional bore and capillary columns, along with column compartment cryogenic cooling.
Visit our contact page or give us a call today to get started!
- On the detection end, we can use:
- FID, which measures ion per unit time making this a mass sensitive detector.
- TCD, which measures the reduction in thermal conductivity when compared to common carrier gases.
- ECD, which measures electron-absorbing components having high electronegativity such as halogenated compounds.
- EP Nitrogen, Low Oxygen
- NPD, which is a very selective method using thermal energy to ionize an analyte having only Nitrogen or Phosphorous in its structure.
- PDD, which is very chemically selective for monitoring high electron affinity compounds such halogen compounds, as well as aliphatics, aromatics, and amines.
- MSD, a mass sensitive detector requiring analyte ionization.
- A brief listing of custom projects we have performed for the pharmaceutical and biotechnical industries includes the following:
- Headspace GC-MS of finished liquid, solid and lyophilized drug product in sterile vials;
- Headspace GC-MS analysis for odor absorbing wound dressing efficiency; and
- Medical gas blends and isotopic enrichment determinations.